How NFV Can Enable 'Pay-as-you-Protect' Network Protection
- Net0, Net1, etc. are routable networks
- The large/thick, curved arrows represent Anycast tunnels that represent the book-ended flow of malicious traffic; with this book-ending, malicious and non-malicious traffic is routed into a Security Pod, and the non-malicious traffic is allowed to continue to the ultimate destination, in accordance with the challenge parameters
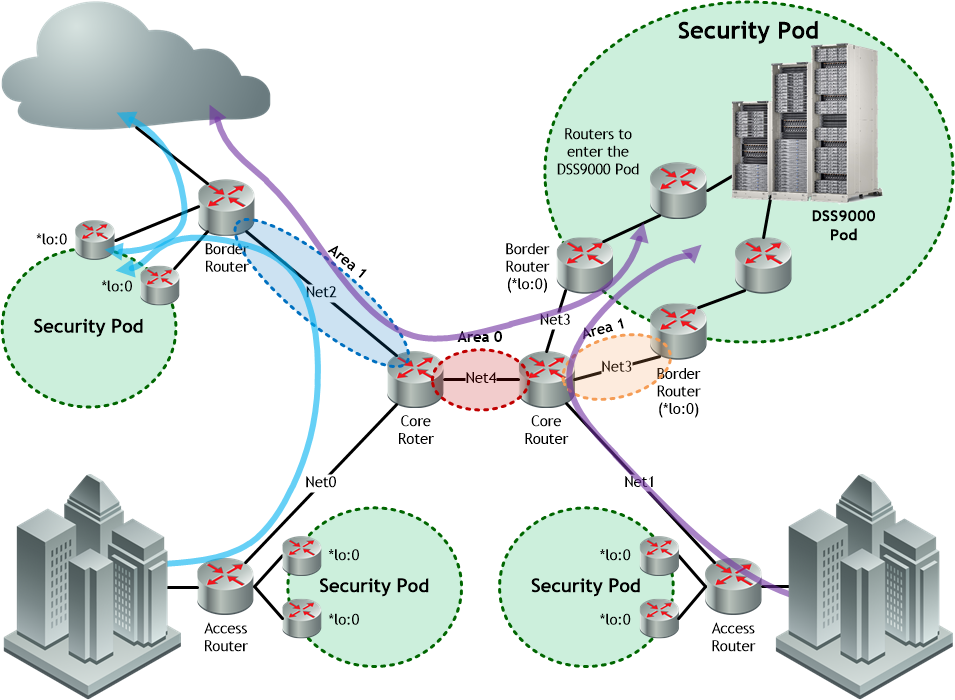
Fig. 1 - Elastically Scalable DDoS Scrubbing
The configuration for the major network elements was as follows:
|
Element |
Configuration |
|
VNF |
Configured to scrub network traffic by detecting and blocking flow flood attacks: |
|
Traffic Steering Engine (TSF) |
Configured to steer all traffic to the available VNFs |
|
MANO |
Configured to scale up a new scrubber (VNF) for every 10,000 new flows per second of network traffic |
Prior to the proof of concept, the network was in a steady state with a mix of traffic spread across a small number of flows. In the steady state, the number of ŌĆśbackgroundŌĆÖ flows fluctuates between about 20 and 30; the active flows represent a mix of traffic types and are of no specific importance to the DDoS scrubbing demonstration itself.
In the first part of the demonstration, a flow flood attack is triggered with a rate of 4,000 flows per second, with a flow timeout of one second; Figure 2 shows the 4,000 attack flows added to the networkŌĆÖs background traffic.
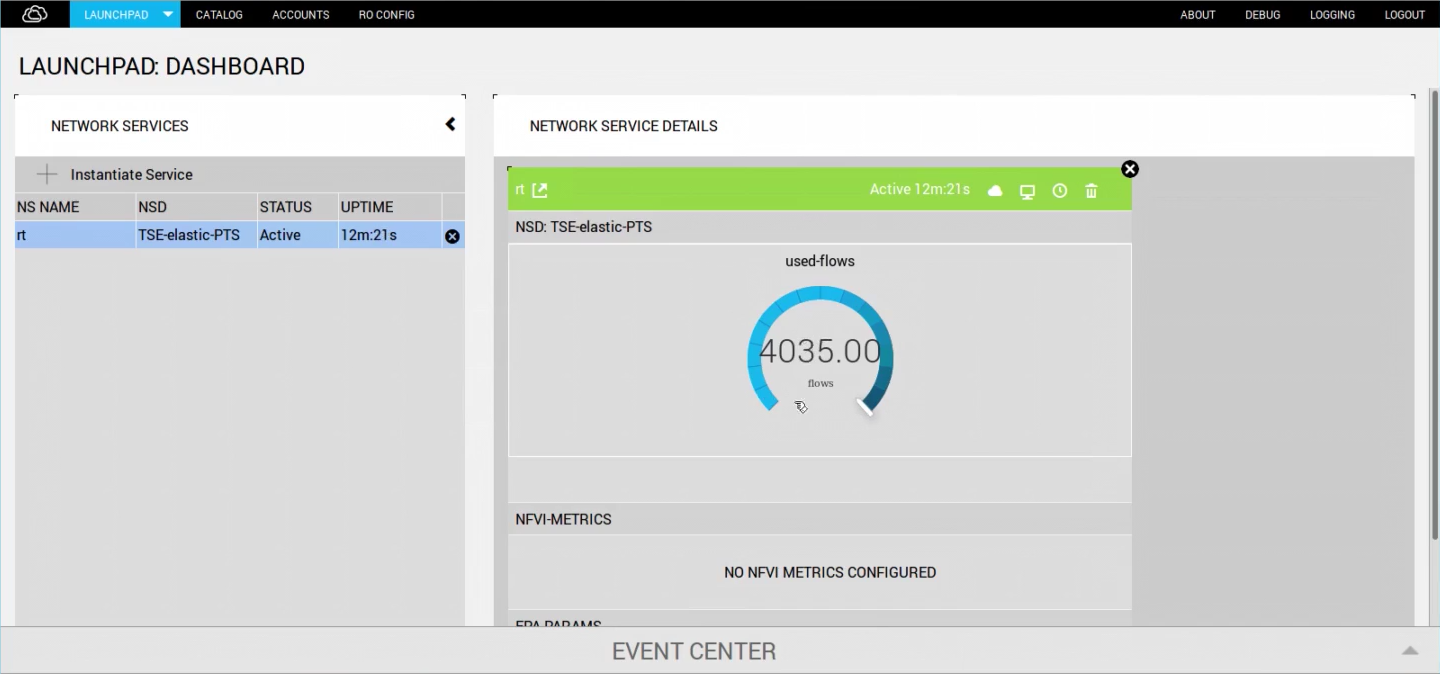
Fig. 2 - Launchpad: Dashboard showing the small attack (4,000 flows per second) during the first part of the demonstration



















