2020 CSP Trends
Sigma Systems’ survey found that, when it comes to digital channels, 62 percent of respondents believe the added complexity of services is having a major impact on the configure-price-quote (CPQ) capabilities of their business. Addressing this is critically important because the impact can be very real: it was estimated that increasing the accuracy and automation of the CPQ process could boost sales by three percent.
To put that into financial terms, automation that increased sales by three percent would increase the sales of tier-one and tier-two operators by $18 billion. There is real money at stake for CSPs that can effectively tackle increasing product complexity during the selling process.
A positive point to take note of is the strong belief that AI can play a major role in this area: 76 percent of respondents believed AI can be applied to improve the sales process and sales conversion rates. The automation of sales processes and increasing levels of AI and machine learning can deliver a highly responsive and effective sales experience.
While there are clear benefits to automation in the sales process as product complexity increases, there is a potential fly in the ointment: 74 percent of enterprise-focused respondents noted a reliance on manual activities and paper-based processes, and 65 percent called out reliance on non-digital channels. The blend of old and new processes and new and legacy systems limits the potential for automation and means CSPs are faced with the need to undertake a broad assessment of these factors as they look to improve sales effectiveness.
Fulfillment Automation
The Create-Sell-Deliver Outlook found a strong link in the minds of CSPs between fulfillment automation and profitability: 78 percent of respondents said automating service fulfillment directly benefits the bottom line, and a striking 86 percent of respondents said the delivery of products to customers has a significant impact on NPS scores.
If automation is seen as a driver of improvement for customer satisfaction, what are the barriers to adoption? Certainly some of it comes down to technology: telco systems are complex, involve legacy software, and changing or replacing them has massive architectural and financial consequences.
But another factor is the rate of change of new offerings being delivered. While we talk about the benefits of bringing new products to market quickly, and the need for CSPs to efficiently sell more complex products and services, actually doing so is placing a strain on their fulfillment capabilities.
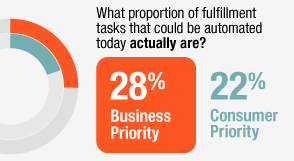 Our survey found a staggering 75 percent of tasks that could be automated were not
automated today (as seen in Figure 2, right). The good news is that there are automation opportunities everywhere. The bad news is that digital-first companies and OTT players have started out
with automated systems, leapfrogging legacy technology and meaning that, once again, CSPs are playing catch-up.
Our survey found a staggering 75 percent of tasks that could be automated were not
automated today (as seen in Figure 2, right). The good news is that there are automation opportunities everywhere. The bad news is that digital-first companies and OTT players have started out
with automated systems, leapfrogging legacy technology and meaning that, once again, CSPs are playing catch-up.
With all the talk of a slew of new products and services enabled by 5G and IoT, the idea that CSPs could still need manual intervention in order fulfilment seems like one from the past. Not so. The survey highlighted that manual intervention was growing as we go into 2020. Around two-thirds of respondents said manual intervention had increased slightly or significantly over the last two years (see Figure 3, below).
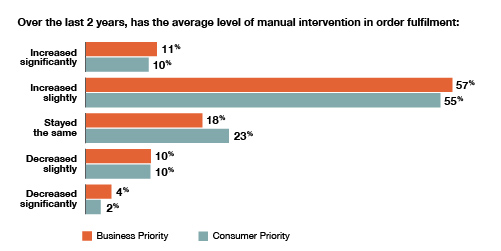
Figure 3 – Change in Average level of manual intervention in order fulfilment
Source: The Sigma Create-Sell-Deliver Outlook, 2nd Edition.
 Manual
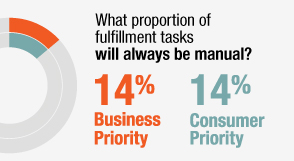
intervention comes hand-in-hand with slow, missed or inaccurate orders. Our survey found that on average, 15 percent of a fulfillment team’s time is devoted to fixing order errors. While
automation is one way to address this, the consensus is that 14 percent of fulfilment tasks will always be manual (see Figure 4, left).
Manual
intervention comes hand-in-hand with slow, missed or inaccurate orders. Our survey found that on average, 15 percent of a fulfillment team’s time is devoted to fixing order errors. While
automation is one way to address this, the consensus is that 14 percent of fulfilment tasks will always be manual (see Figure 4, left).



















