RIS: A Key Building Block for 6G
An illustrative diagram of RIS is provided in Figure 1 (see page one). It depicts RIS as a new system node dynamically configured by the system controller, which turns the wireless environment from a passive to an intelligent actor such that the channel becomes programmable. A comparison of RIS and its unique characteristics against other wireless technology concepts is provided in Figure 2. RIS will challenge basic wireless system design paradigms, creating innovation opportunities that will progressively impact the evolution of wireless system architecture, access technologies, and networking protocols.
Global RIS research projects
RIS has attracted a lot of global attention in the research community, especially in Europe. There are already several European collaborative research and innovation projects working on this topic such as AIMM, ARIADNE, DAEMON, HEXA-X, and RISE-6G, to name a few. The members of these projects include a wide range of network operators, telecom equipment vendors, and research institutes.
In addition, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Communication Society has launched two special interest groups and one emerging technology initiative on RIS; these are RISE SIG, REFLECTIONS SIG, and RIS ETI. There have also been prototyping and testing results for RIS, including metasurface reflective arrays demonstrations, for example by NTT DoCoMo, Orange, MIT, and the University of Surrey.
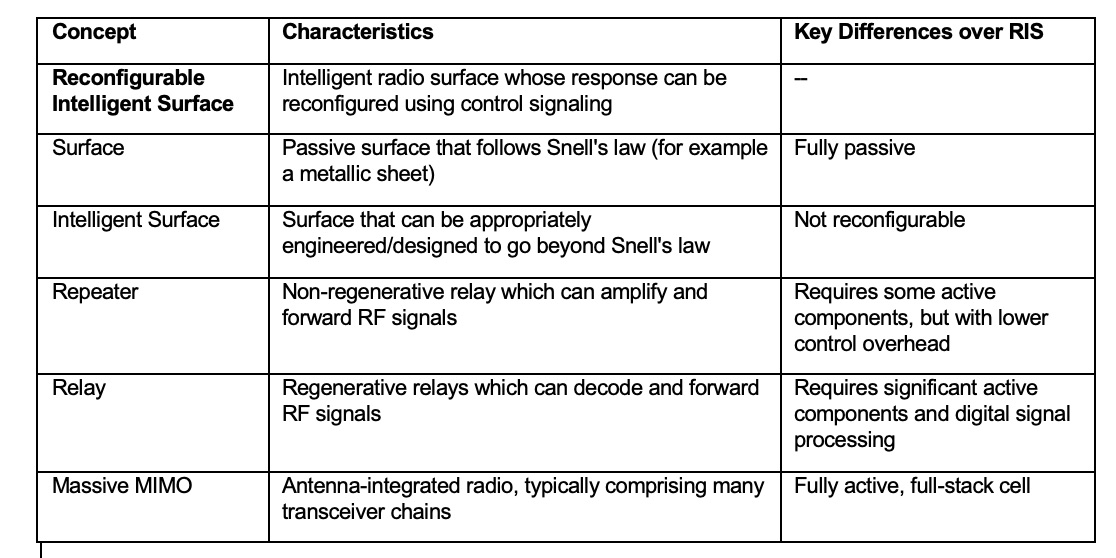
Figure 2. Unique characteristics of RIS against other wireless technology concepts
click to enlarge
RIS technology is supported as a key technology trend in the International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) IMT-2030 Future Technology Trends report. There have also been early attempts recently to bring RIS for exploratory studies in standards development organizations including 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and IEEE.
While extensive research efforts are ongoing on the topic, global standardization of RIS is still at its very early stages. There are many technical challenges that need to be adequately addressed before RIS can be adopted into future standards, toward eventual commercialization of the technology.
ETSI, which produces globally applicable standards for ICT, has launched a new Industry Specification Group on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (ISG RIS). The group has been created to review and establish global standardization for RIS technology. This initiative was formed to streamline pre-standards research efforts on RIS technology across various EU and UK collaborative projects, extended with relevant global initiatives toward paving the way for future standardization of the technology.
ETSI ISG RIS, which launched in September 2021 with a duration of two years, will identify and describe RIS-related use cases and deployment scenarios, specify derived requirements, and identify technology challenges in several areas, including fixed and mobile wireless access, fronthaul and backhaul, sensing and positioning, energy and electromagnetic field (EMF) exposure limits, security, and privacy. The group will clearly document a networking e2e reference architecture including RIS elements, describe RIS-based specific deployment practices and guidelines, provide a gap analysis for RIS microelectronics and enabling technologies, and make proofs of concepts. The ISG activities and deliverables will be complementary to existing ETSI work and relationships with other ETSI bodies, and the wider industry will be established to avoid duplication, maximize synergies and act to ensure broad industry adoption of RIS, a key technology trend for future wireless systems.
Further information on the ISG RIS scope, work program, and deliverables can be accessed through the ISG RIS Portal.



















