Edging Closer to Open Telecom Networks with Open RAN
The RAN is also evolving from distributed and integrated to virtual and centralized, where baseband units (BBUs) are pooled outside of the traditional macro base station—enabling the evolution that moves workloads towards the edge.
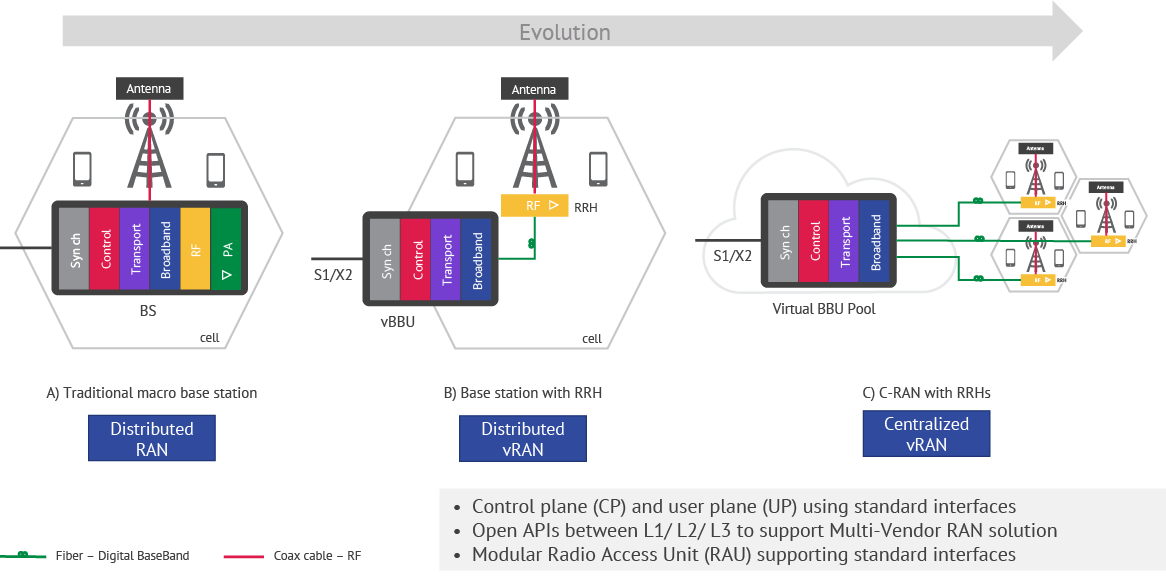
Figure 2. RAN Evolution
(click to enlarge)
Some workloads—such as cloud-assisted car driving (autonomous vehicles), VR gaming, and high-frequency trading—have significantly reduced latency requirements, meaning that they can only be deployed at the edge. At the same time that latency is going down, mobile bandwidth requirements are increasing. Open virtualized RAN and edge architectures for 5G networks deliver key capabilities, including:
- Virtualized mobile core for 4G and 5G networks with end-to-end network slicing
- Programmable RAN control plan using open reference architectures
- Centralization and virtualization of RAN eNodeB functions plus mobile edge apps
- Unbundled RAN (CU/DU) using standard APIs, and
- Modular Remote Radio Unit (RRU) software functions, supporting multiple RAT co-existence.
There are a number of standards organizations and open source communities that have emerged to advance open and disaggregated RAN architectures.
- 3GPP is included in this list as it is the standards-setting body for 5G driven by the service providers, and it is committed to meeting service provider requirements and enabling successful commercial 5G deployments. New open architecture ideas often first percolate in 3GPP.
- Open Networking Foundation (ONF) – under the CORD (Central Office Re-architected as a Datacenter) umbrella, it has integrated multiple open source projects that focus on service providers’ needs for its mobile, residential, and enterprise customers. At the access level, it has delivered open reference architectures for M-CORD (Mobile CORD) and R-CORD (Residential CORD), as well as enabling access-technology-agnostic open solutions with Multi-Access CORD.
- Telecom Infra Project (TIP) was founded to initially focus on simplifying and disaggregating the RAN. It delivers open hardware for telecom network infrastructure.
- xRAN delivers another approach to disaggregating the RAN by delivering an eXtensible software-based solution that can rapidly respond to real-time user needs. It extends the RAN with specific north and southbound SDN interfaces.
- ORAN Alliance is the newest addition to this list. Launched in February 2018 by global tier-one service providers, the Alliance is focused on driving openness into the RAN for next-gen networks, thereby making the networks smarter. ORAN extends the efforts of the C-RAN Alliance and the xRAN Forum.
Open and disaggregation are critical to this RAN evolution. By disaggregating the RAN into separate components, service providers will be able to swap components in and out from multiple vendors, reducing vendor lock-in and allowing them to choose from best-of-breed solutions to meet their specific network requirements.



















