Edging Closer to Open Telecom Networks with Open RAN
By: Prakash Siva

The telecom industry is undergoing a significant transition as service providers and infrastructure vendors are turning to open source and multi-access edge computing (MEC) solutions to meet the demands of 5G—and to reduce costs and accelerate service innovation. Open RAN solutions are gaining traction with service providers that are driving disruption in their networks.
5G in the Driver’s Seat
The fourth Industrial Revolution provides a roadmap for the evolution of technology—moving from connected hardware in the 2G/3G era to connected people with LTE/4G, to connected everything with the advent of 5G.
For service providers, 5G services and applications will put unprecedented pressure on their networks to meet demands to support 50B connected devices, 1000x mobile data volumes, 5x lower latency, and 10x to 100x end-user data rates. As such, the transition to 5G is one of the key market drivers for Open RAN solutions. Because the transition to 5G will bring a lot more traffic onto the network, service providers need an access technology that will be able to keep up with bandwidth demand. By their very nature, open technologies are more cost-effective than single-sourced proprietary solutions. By leveraging Open RAN technology, service providers will be better able to manage explosive traffic growth and channel resources toward new services and innovation.
About Radisys
Radisys, a global leader in open telecom solutions, enables service providers to drive disruption with new open architecture business models. Radisys’ innovative disaggregated and virtualized enabling technology solutions leverage open reference architectures and standards, combined with open software and hardware to power business transformation for the telecom industry, while its world-class services organization delivers systems integration expertise necessary to solve communications and content providers’ complex deployment challenges. For more information, visit www.Radisys.com. Keep up to date with Radisys: Follow us on Twitter
Disaggregation is the Key
When it comes to enabling the evolution to 5G and meeting service providers’ cost and innovation goals, the traditional RAN architecture is problematic. It is proprietary, embedded, fixed or pre-programmed, and integrated, resulting in high-cost last-mile transport. All of these characteristics make traditional RAN architecture difficult to change and are reasons that the RAN is the last area of the network to become open.
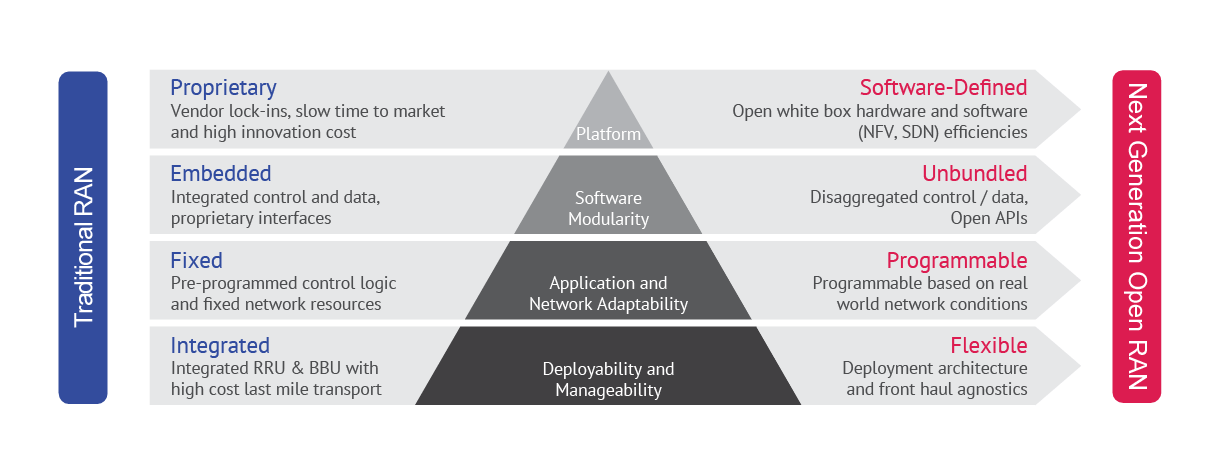
Figure 1. RAN Re-Architecture: A Must to Evolve to 4G and 5G Networks
(click to enlarge)
However, next-generation Open RAN solutions are gaining ground. By disaggregating the RAN components and leveraging open solutions, service providers can utilize a flexible solution that can address real-world network conditions.




















