Disaggregation: The Foundation
for Agile Networks
A disaggregated RAN solution includes three main elements: the centralized unit (CU), the distributed unit (DU), and the radio unit (RU).
Figure 5 below highlights the use cases supported by Open RAN, as well as options for the DU and CU to either be both on premise, or to be separated with a centralized cloud-based CU.
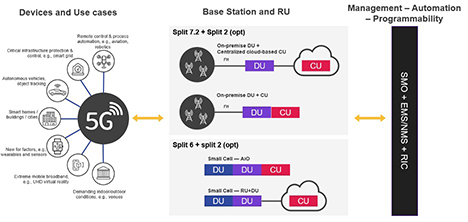
Figure 5: Open RAN supports many use cases
click to enlarge
Increased agility and automation are achieved via the O-RAN Alliance’s Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) platform, which supports automation at scale. The introduction to the network of the O-RAN Alliance’s real-time RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) also enables increased automation and changes how the RAN is managed and optimized. An open and disaggregated RAN supports edge computing and IoT by enabling the colocation of the RAN and core user plane closer to the end subscribers to support low latency use cases.
Disaggregated private network use case
With the arrival of Industry 4.0 and the digital transformation of industries, there is an increased push towards private network deployments, which can enable increased automation, efficiency, and security.
Many of these private 4G/LTE and 5G networks are increasingly based on open and disaggregated architectures. These private networks rely on available spectrum—such as locally licensed, shared (CBRS) or unlicensed spectrum—and can be deployed via small cell technology, micro or macro networks, or in-building DAS solutions. Figure 6 on the next page shows a complete private network that supports moving the user plane function closer to the end users.
The role of systems integrators
Once a network is disaggregated, the components need to be integrated back together for seamless end-to-end functionality and performance. Disaggregated systems require even more validation than traditional monolithic systems as the components are selected from a multi-vendor ecosystem. Systems integrators can play a key role to optimize this complex process while ensuring timely and on-budget delivery of the complete solution.
The use of open, standardized interfaces helps streamline the process, making it easier to aggregate the various components. At the same time, they enable easier development of automated systems for solution validation. A systems integrator such as Radisys that also builds open standards-based broadband and RAN products can deliver additional value to CSPs by bringing to the table deep knowledge of industry


















