Closing the Top Five Cybersecurity Gaps
From a cybersecurity standpoint, these can cause security breaches to occur and spread. The key to solving human error is to reduce the need for humans to intervene and thus the risk of introducing mistakes. For large tech organizations, this means completely removing the human element because of the need to scale to and operate thousands of nodes. To do so requires capturing the decision matrix and using automation to address both categories of error and minimize the risk that humans introduce.
Seamless cybersecurity: hyperautomation, open cybersecurity platform, and out-of-band
The problems above have a common thread: they lack a seamless way to automatically deploy the right combination of different products at various locations. To address this gap, tech giants have taken a three-pronged approach that includes hyperautomation, an open cybersecurity platform, and out-of-band infrastructure.
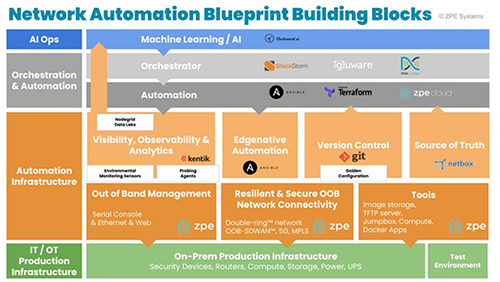
Figure 2: Network Automation Blueprint Building Blocks
(Click to Enlarge)
Hyperautomation is important because it enables many IT and business workflows to be automated, using orchestration technologies that greatly reduce manual workloads and the risks of human intervention. An open cybersecurity platform is critical for hosting an organization’s choice of physical and virtual solutions, allowing agile operations and reducing the need for many physical devices in the stack. Private out-of-band management infrastructure is the final key piece to safely managing and recovering systems—and allowing IT teams to gain manual control of their automation pipeline when necessary.
However, implementing these concepts comes with a high degree of ambiguity, given there is no correct reference design available. This has led to the development of a validated reference design called the network automation blueprint, which is a key enabler for organizations that wish to achieve holistic cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity with the network automation blueprint
The network automation blueprint is made up of four major building blocks (see Figure 2 above).These create a management network design pattern to accommodate Gartner’s definition of hyperautomation and allow organizations to stitch together a seamless fabric of various cybersecurity solutions. The blueprint’s building blocks are:
IT/OT production infrastructure: This includes discrete servers, switches, routers, NGFWs, and common production equipment. To prevent device proliferation, it’s recommended to
use the open cybersecurity platform approach. This platform enables a single piece of hardware to host multiple security and network functions (NGFWs, SD-WAN, user experience monitoring), which
can be automated in a zero-touch fashion from a centralized cloud orchestrator.


















