How Rich Communications Enables the Next Generation of Connected Apps
RCS makes friends out of enemies
In 2012 the GSMA also debuted the RCS API initiative, giving birth to the RCS service-delivery API (application programming interface). The concept of API allows app developers to do what they do best — develop great apps — while service providers do what they do best — offer rich communication services that are reliable, high performance and always on, and fully leverage the capabilities of next-gen mobile devices and networks.
A key positive differentiator of the RCS API is that it converts the entire world of over-the-top (OTT) applications — which have been a thorn in the side of carriers — into a carrier’s best friend, and vice versa. Developing exciting new applications for consumers requires creativity and innovation, and to date that hasn’t been the forte of carriers, nor has the development of robust real-time communication and digital signal processing (DSP) subsystems been high on the list of mobile app developers. The RCS API enables each to do what they do best. In the new paradigm carriers are neither a dumb pipe nor mere distributors of apps — they are suppliers of rich communication services.
RCS application architecture
The RCS client framework must first perform an IMS registration, at which time the client is authenticated and the service capabilities of the client identified. Upon completion of IMS registration the application can utilize any of the rich communication capabilities, and multiple applications can use these services simultaneously (Fig. 1).
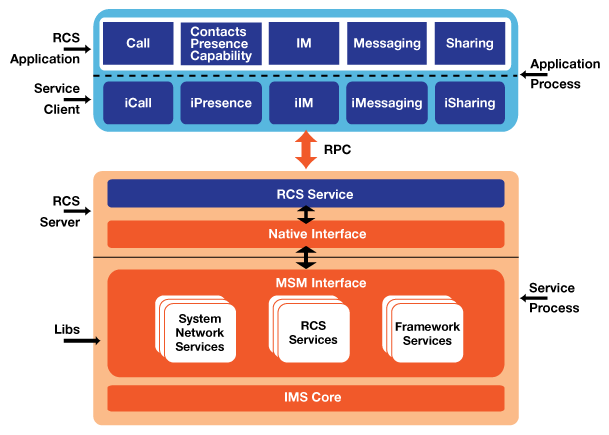 Fig. 1: RCS application architecture
Fig. 1: RCS application architecture
An application may first use the network address book to select contacts to communicate with, then check the presence information to identify both the capabilities of those contacts on their current devices (capabilities exchange) and the status of the contacts (“busy,” “in a meeting,” “available”). Then the application may engage those who are available. It can also engage users in gameplay, file sharing, and real-time multiparty video, audio chat and so on.
Performance matters
Historically speaking, OTT applications have yielded only best-effort service for voice and video, and generally haven’t offered the best battery life for these real-time, processing-intensive functions. By being tightly integrated with regular cellular service, which works everywhere, RCS can significantly outperform current OTT applications and produce a superior rich-communication experience by offering higher-quality voice and video and better battery life, which requires full leverage of both the capabilities of the service provider’s infrastructure and those of the end user’s device.



















