Powering Innovations Untether Optical LANs
One advantage of DC microgrids is that they eliminate the need for power conversion from AC to DC, which is required by many IoT devices such as sensors, cameras, and other low-power devices. This eliminates the inefficiencies and losses associated with conversion, which can be significant when dealing with large numbers of devices.
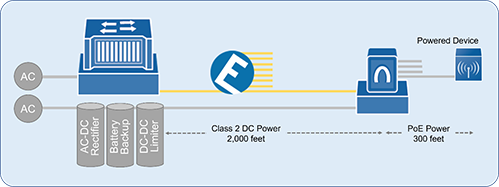
Figure 3: An Optical LAN using Class 2 power to connect an ONT out 2,000 feet
Another advantage of DC microgrids is that they can be easily integrated with renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines, which generate DC power. This makes them an ideal choice for modern buildings that are designed to be sustainable and energy efficient.
DC microgrids can be built in different configurations, such as centralized, decentralized, or hybrid. In a centralized configuration, a single DC power source supplies energy to all devices in the network. In a decentralized configuration, each device is equipped with its own DC power source, such as a battery or a solar panel. Hybrid configurations combine both centralized and decentralized systems to realize the benefits of both. DC microgrids are an effective way to power Smart Buildings and IoT networks, offering advantages such as energy efficiency, scalability, and flexibility in integrating with renewable energy sources that align well with Optical LAN attributes.
Passive Optical LAN – With all these powering innovations unleashing Passive Optical LAN architecture to its full potential, and connecting Ethernet end-points miles away, enterprise businesses are now able to make huge advancements in scalability, security, stability, and sustainability.
Optical LAN provides better scalability by using passive optical splitters to distribute the signal from a single optical fiber cable to multiple devices, without requiring any power. This makes it a cost-effective and efficient way to distribute the signal, with minimal signal loss, allowing Optical LANs to support a profusion of Ethernet connectivity over long distances. Additionally, Optical LANs allow in-building networks to be designed with either a reduced number or total elimination of telecommunications rooms. Fiber-based LANs offer enterprise networks greater security by promoting the use of optical cabling, which is inherently more secure than copper cabling. Unlike copper cables, fiber cables are immune to electromagnetic interference and cannot be easily tapped, making them more difficult to intercept or disrupt. Furthermore, Optical