Wireless Sustainability
By: Nazim Choudhury

In this century, few issues have dominated our collective consciousness as much as climate change and environmental sustainability. Only recently, however, has the communications industry recognized its responsibility to help solve this incredibly complex global issue. Energy use continues to strain multiple industries, driving up costs and imposing constraints on growth that can be avoided. For most major economies, even switching from incandescent to LED lighting can save the economy billions of dollars in reduced costs (Development Research Center of the State Council; World Bank, 2022), so there is a significant business incentive to see energy reductions across the board. The wireless industry is no different, with multiple groups, companies, and governments quickly realizing that it has its own role to play in building a more sustainable industry.
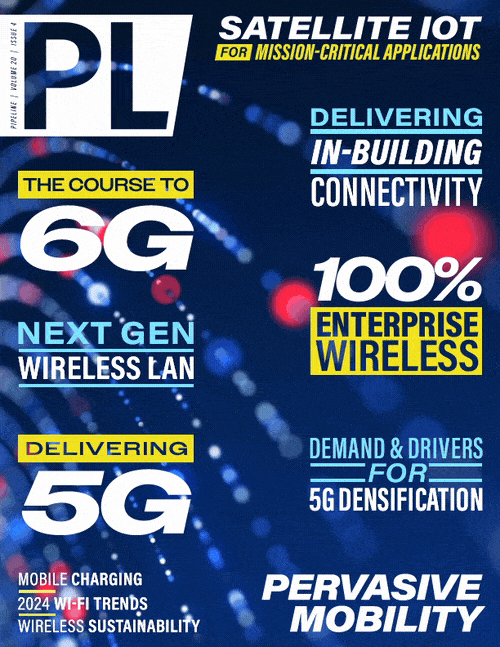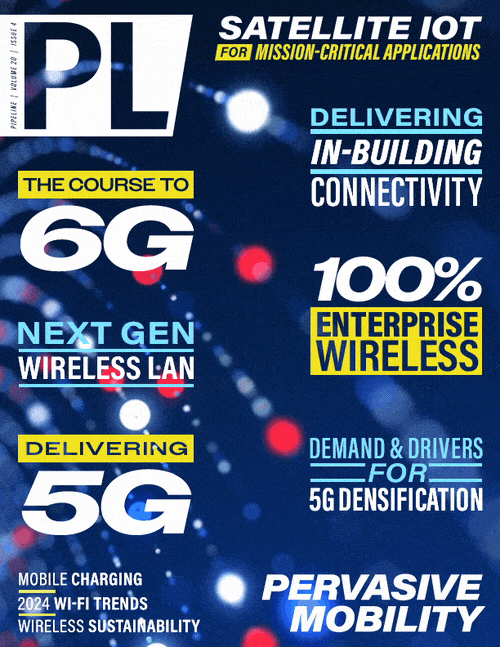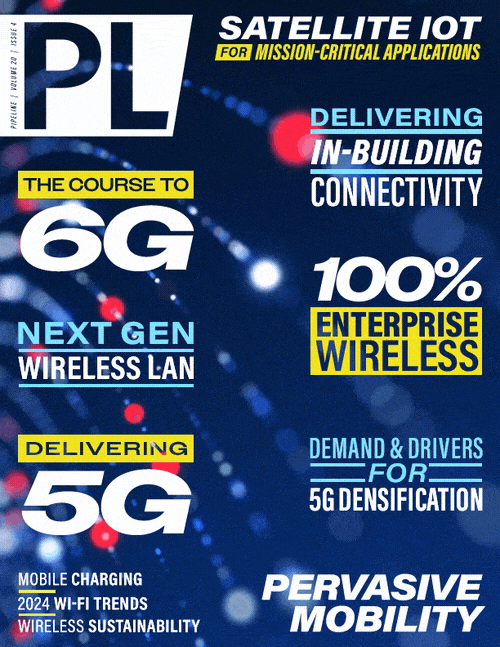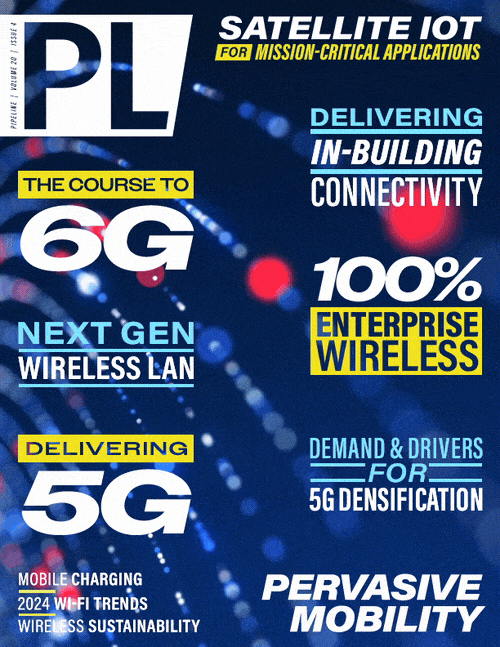
Like all industries, the wireless sector is definitely consuming significant energy resources. The information/communications/technology market has steadily consumed more and more electricity, with more growth in sight as we move from 5G to 6G and beyond. Adding billions of new devices to the network (via the IoT and other means) will significantly increase this burden. By some estimates, the communications industry is set to consume almost 20 percent of all energy resources by 2030. (Figure 1)
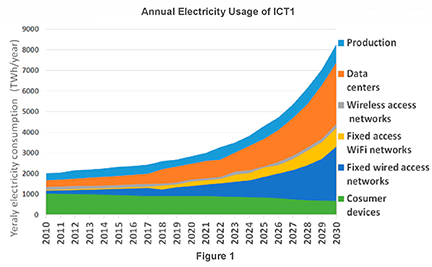
Info/Comm/Tech projected energy usage as a percentage of total electricity is notable! 1. Lorincz, Josip, Antonio Capone, and Jinsong Wu. "Greener, energy-efficient and sustainable networks: state-of-the-art and new trends" Sensors, (2019): 4864.
This increased energy usage has not gone unrecognized within the wireless market. In this era, the telecommunications industry is awakening to its role in addressing climate change and sustainability concerns. As we transition from 5G to 6G and beyond, there's no denying that the industry is consuming significant energy resources. However, the potential for technology to drive efficiency and sustainability across multiple sectors is enormous. Take 5G, for instance, which is already demonstrating its capacity to reduce energy needs and enhance productivity in various industries, including energy management in smart buildings and Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing sector. Beyond our own infrastructure, these advanced upcoming technologies are enablers for tremendous amounts of energy consumption savings and sustainability in almost every industry, transforming the telecommunications providers into agents of change as well. These are clear illustrations of how advanced technologies are poised to mitigate energy-related challenges.
Sustainability via New Technologies
More than most, our industry has advanced technologies at its disposal that have great potential to reduce our own environmental impact, as well as that of our customers. 5G is already being deployed in use cases worldwide that reduce energy needs and increase efficiency and productivity for multiple industries. Energy management in smart buildings is already a clear application, seeing results in several markets. Singapore has deployed 5G for energy management across numerous smart buildings and is seeing excellent results (Energy and AI, January 2022).
The manufacturing industry is actively evaluating 5G to enable Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). A recent study by ABI found that 94 percent of key decision-makers across 12 industrial segments agree that IIoT can improve overall energy efficiency. Moreover, 72 percent are looking to increase spending on this technology due to its impact on sustainability. Energy management, waste management, extending equipment life, and emissions monitoring and control are just a few of the environmental benefits that 5G helps to enable.
These IoT benefits also extend to the agriculture industry, as 5G-enabled IoT sensors can contribute to sustainable food production practices. Collectively known as precision agriculture, these wireless-enabled systems collect and analyze data on moisture, sunlight, air quality, and other factors that influence crop growth. Moreover, 5G wireless tools help reduce the use of pesticides and fertilizers by informing farmers to dispense them solely where necessary, not across entire fields.