Understanding M-CORD: Re-architecting Mobile Infrastructure for 5G Services
By: Joseph Sulistyo

Service providers are turning to software-centric architectures with the principles of Software-defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) to unlock their constrained and disjointed network infrastructure. They are seeking to transition from a closed architecture with complex control and interoperability to a more open and efficient software-driven network and service architecture running on open, commodity platforms. This approach is driven by service providers’ requirements for their networks to enable an agile service-driven environment that can dynamically respond to real-time subscriber demands.
CORD (Central Office Re-architected as a Datacenter) is a progressive open source project of the ONOS (Open Network Operating System) partnership. It combines NFV, SDN and the elasticity of commodity clouds to bring datacenter economies and cloud agility to the Telco Central Office. In a legacy Central Office, infrastructure was built using “black box” solutions that locked service providers into a single vendor. In the CORD framework, commodity servers and “white box” switches are coupled with open source software, including OpenStack, Docker, ONOS and XOS to deliver an extensible platform that supports a variety of applications.
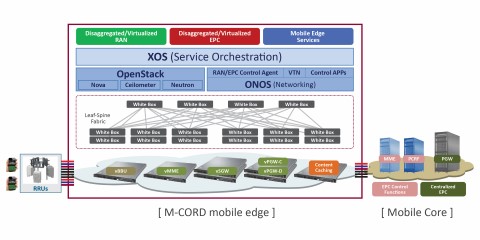
Mobile Cord or M-CORD is a reference implementation for mobile services at the network edge. M-CORD integrates the open CORD framework into the service providers’ mobile network architecture to enable an agile, service-driven mobility infrastructure that is much more controllable, programmable and flexible for new innovation by operators. The three key components of the M-CORD, as seen in Figure 1 below, are:
- Disaggregated/Virtualized RAN
- Disaggregated/Virtualized EPC
- Mobile Edge Services
Figure 1: M-CORD Architecture
(click image to expand)
M-CORD: The Next Evolution of 5G
The increasing demand for mobility at the edge brings its own set of challenges. Traffic at the edge continues to grow exponentially, and with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) and this trend has no end in sight. Current network infrastructures can’t keep up, limited by vendor lock-in, scarce spectrum availability as well as overloaded backhaul networks. The M-CORD infrastructure solves these challenges by utilizing SDN and NFV technologies to enable integration across diverse solutions. It transforms traditional EPC and RAN components into modular, disaggregated services that can be delivered and instantiated on demand at the edge under the CORD framework. By advancing a service-driven cloud edge infrastructure, M-CORD sets a critical path towards 5G.