Ransomware Explained
In September 2019, 22 cities in Texas were hit with ransomware. The attackers demanded $2.5 million to restore encrypted files, leading to a federal investigation. These stories are examples of the reality that ransomware attacks are especially prevalent in financial and healthcare organizations. It is estimated that cyber criminals targeted 90 percent of these businesses last year.
The course of an attack
Ransomware begins with malicious software being downloaded by an unwary person through an infected email or link onto their computer or smart device.
Once ransomware infects an endpoint, it will run freely wherever it has access. In seconds, the malicious software will take over critical processes on the device, then search for files to be encrypted, meaning all the data within them is inaccessible.
The ransomware will then infect any other hard drives, network attached devices and so on, taking out everything in its path—including backups.
This entire process happens extremely quickly. In just a few minutes the device will display a message that looks like this:
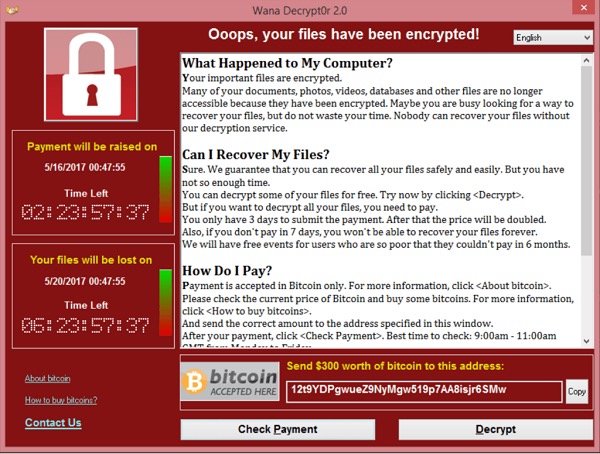
Figure 1: WannaCry Ransomware Attack
This is the message that was displayed to users who were infected with the WannaCry ransomware attack. As you can see, it’s a ‘cyber blackmail’ note. Users are informed that they have been locked out of their files, and they must pay to regain access.
Ransomware risks
The people within your organization are often your biggest security risk. The major issue here is a lack of awareness and staff education about security threats. Many people are unaware of what threats look like, and what they should avoid downloading, leaving you open to risk.



















