The Evolution of Wireless Networks: Shift from Hardware-centric to Software-centric
To take advantage of resource pooling and spectral efficiency, many wireless operators are looking at Centralized RAN (C-RAN) where the resources are centralized and aggregated in a central location to support many remote radio heads. With the baseband processing in a centralized location, each cell is controlled by a scheduler that allocates radio resources to the various locations based on user demand. In comparison to the traditional distributed RAN architecture, C-RAN provides significant economic benefits through resource sharing including power consumption reduction, smaller footprint, lowered site leasing cost, and enhanced coordination between cells. (Figure 2).
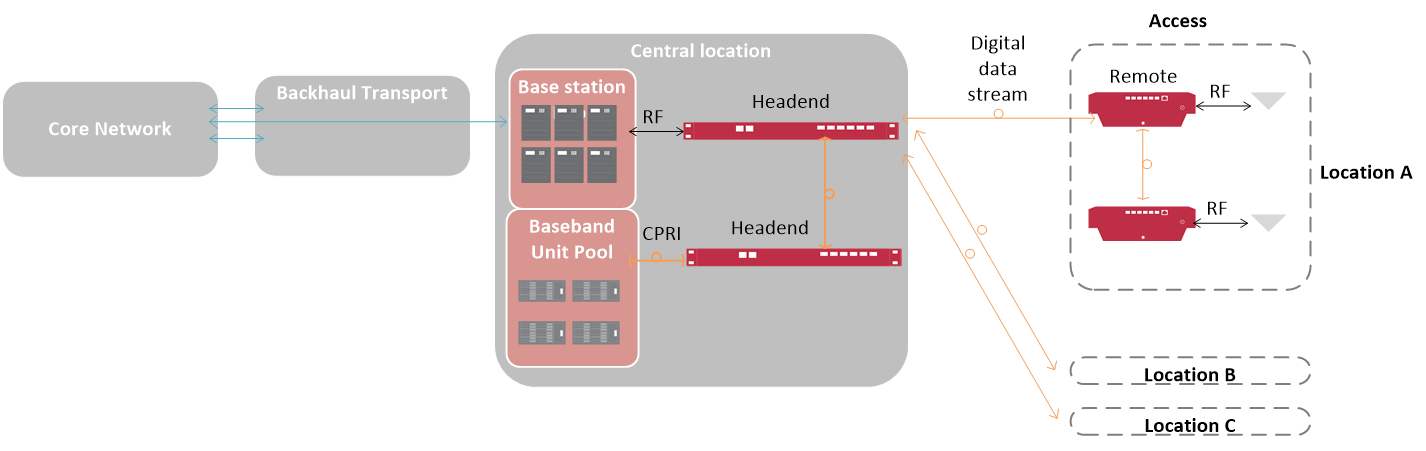 Figure 2. Centralized RAN (C-RAN) architecture
Figure 2. Centralized RAN (C-RAN) architecture
Virtualized RAN:
RAN Virtualization can be seen as the natural next step where the content routing configuration, and the control and monitoring (C&M) functionality of the network elements will be virtualized in a web-scale data center. By taking advantage of the Software Defined Networking (SDN) concept where the network control is separated from the data forwarding functions, it enables rapid reconfiguration of the network and dynamic traffic balancing. With the C&M of the network elements virtualized in the cloud, the configuration and management of the network can be done remotely and on demand, which ultimately makes it easier to configure and maintain the network.
With a software-defined Virtualized RAN, multiple data streams of licensed spectrum, unlicensed spectrum, and other content can be delivered to the remotes from a web-scale data center. Similar to the virtualized server and storage infrastructure of data centers in cloud computing, wireless operators can direct multiple data streams of content from a centralized intelligent switch without having to touch the individual switches. The delivery of data streams wherever and whenever they are required in the network enables wireless operators to have complete control over network traffic flow and better manage the traffic loads in a flexible and efficient way (Figure 3).
RAN Virtualization can sometimes be referred to as Cloud RAN, or C-RAN. However, it is very unlikely that the wireless operators will use public cloud space for core network functions; therefore, RAN Virtualization is a preferred way in many instances.
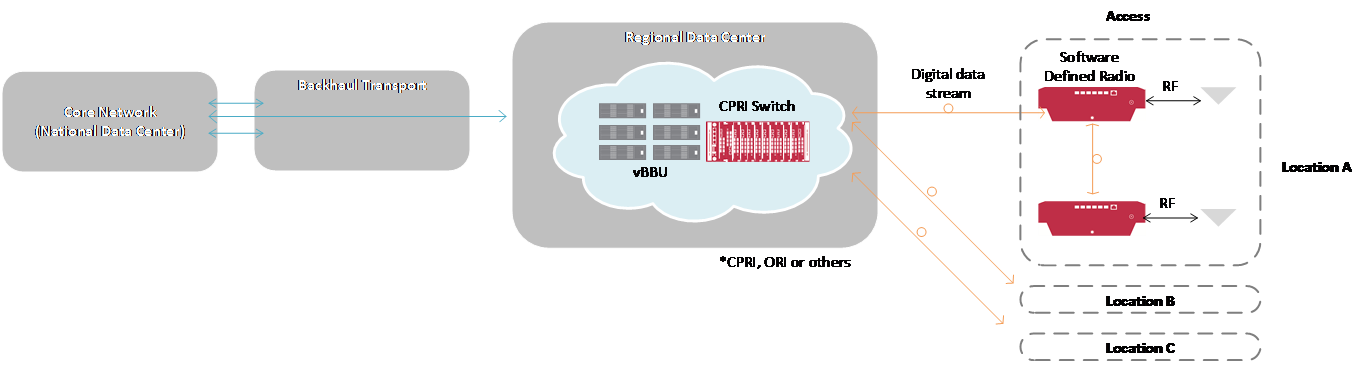 Figure 3. Software-defined Virtualized RAN
Figure 3. Software-defined Virtualized RAN
The drivers for a software-defined virtualized RAN
The ultimate driver for Virtualized RAN is the significant reduction in cost and increase in flexibility. Spectrum is a limited, finite resource; it is often referred to as “invisible gold”. With RAN Virtualization, radio resources are virtualized and any spare capacity sitting idle can be switched to when and where it’s needed most. This eliminates over-provisioning and enables higher utilization of network resources thus providing CAPEX and OPEX savings.



















