Mobile Networks: Navigating the Perfect Storm
By: Dean Mechlowitz

Mobile service providers face growing operational challenges from new 3G, 4G and 5G technologies and massive radio access network expansion from small cells. Backhaul complexity has also increased dramatically with the transition to Ethernet/IP. New business models resulting from Machine-to-Machine (M2M), Internet-of-Things (IoT) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) further complicate operations, while increasing customer expectations increases service assurance challenges. Operators are racing to introduce new services, maintain network quality, and improve costs. Moreover, network and service quality is directly linked to customer loyalty and operational efficiency is directly linked to profitability.
Mobile operators spend approximately 15 billion dollars annually dealing with outages and degradations. This equates to roughly 1.5 percent of annual revenues. Configuration-related issues are the cause for over 40 percent of outages and degradations (sources: HeavyReading and NetScout). A large percentage of congestion and overload scenarios are also as a result of poor or outdated network configurations. Some analysts, such as the Yankee Group, have attributed 62 percent of network downtime to be the result of misconfiguration.
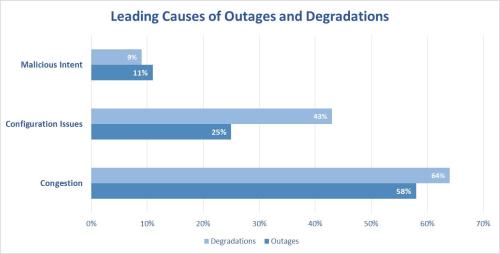
Figure 1: Most common causes of Mobile Outages and Service Degradations
Business impacts and why this matters
Subscriber churn is the single biggest cost associated with network outages and service degradations. The impact is larger in developing markets. Globally, network quality is the 3rd most significant contributing factor to churn. Faced with increased competition from other operators, over the top providers and more demanding subscribers; acquiring and retaining customers is critical. Existing customers spend more, purchase higher-margin products and services, and are more likely to refer additional customers. It costs an average of 250 dollars for a mobile operator to acquire a new customer in developed markets. Many operators are losing around a quarter of their customers annually and so it is not uncommon to have to wait more than 12 months to break even on a customer. For a typical mobile operator, a monthly 2 percent churn rate means average customer life time of 50 months. If average revenue per user (ARPU) is close to 30 dollars per month, then the average lifetime value per customer is around 1,500 dollars. Decreasing churn means increased lifetime and value. A 5 percent increase in customer retention has been shown to translate into approximately 25 to 55 percent increase in profitability. For example: if we assume a mobile operator with 1.5 million net additions in the year, ARPU of 39 dollars, and a 3.5 percent quarterly churn rate; then decreasing churn to 3 percent would deliver an additional 40 million dollars of revenue and 22 million dollars in profit in just 36 months.It is important not to overlook backhaul, network performance and quality. Inadequate backhaul capacity and poor quality backhaul are responsible for approximately 50 percent of network performance problems. Poor network service is responsible for 14 to 40 percent of churn depending on the operator. Strategy Analytics estimates that investment in improved backhaul could reduce a mobile operator's churn rate by between 4 and 7 percent - depending on the region, a net reduction in churn of 1.2 to 2.1 percent. There is a distinct need for more dynamic network reconfiguration to share and steer traffic load across multiple network links as traffic fluctuates in order to ensure consistent Quality of Service (QoS) for end users.
Mobile operators incur high operational costs when troubleshooting the network configuration issues which are causing network outages and degradations. Pinpointing the location and specific misconfigured parameters is time consuming, and usually requiring skilled, high-cost network support personnel. Because service issues span multiple technologies, such as RAN and backhaul networks, input from multiple subject matter experts is often required.



















