Enabling the Mesh of Pervasive Connectivity
Lower-power access nodes with a shrunken profile aren't new, but the way they are being used has changed. "While small cells, including microcells and picocells, have been used for the past two decades to improve voice coverage, now mobile broadband is shifting the game to capacity upgrades," wrote Stéphane Téral, Principal Analyst for mobile infrastructure and carrier economics at Infonetics Research.
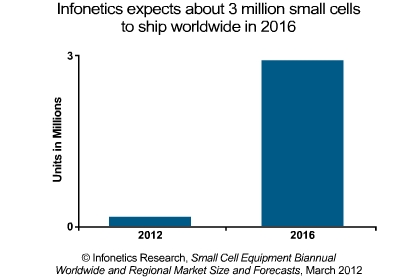
Small cells are a critical component in the mesh of wireless connectivity. "...the chief objective is to complement and enhance the macro-cell layer from a capacity standpoint with a new breed of low-power nodes like public space femtocells and Wi-Fi,” explained Téral in a statement.
Don Bowman of Sandvine agrees that this is the era of the small cell. “There is no question in my mind that small cells are here,” Bowman said. “Small cells are [also] going to be heavily used in indoor technologies,” he added.
Same Network, Different Flavors of 4G
Small or large, the access nodes of the future are being built to support multi-mode operation. Alcatel-Lucent's lightRadio, for instance, comes in micro and macro sizes, and supports 3G, 4G, and Wi-Fi. Similar offerings are available from Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia Siemens Networks. But what's interesting is that some operators are using multiple flavors of 4G simultaneously in order to leverage legacy assets and widen their nets.
Sprint announced a hotspot last month that operates on 3G, LTE, and WiMAX. This was Sprint's answer to the question posed by many reporters: What are you going to do with WiMAX as you move to LTE?
Even though LTE has emerged as the 4G champ, it is important that we don't neglect the capabilities of WiMAX. WiMAX is more than just Wi-Fi on steroids. It offers wide coverage, can be effectively used for municipal and large enterprise networks, offers high bandwidth, and can be less expensive than LTE deployments. It's also the predominant form of 4G in many developing areas of the world. Adding the WiMAX piece to the connectivity puzzle greatly enhances the capabilities and reach of tomorrow's networks.



















