Frames that are received from the IP/MPLS network port are classified based on the EXP field in the shim header of the label stack.
An important aspect of providing a VPLS service over an ATM VC is the ability to achieve the desired QoS objectives for the service. When Ethernet frames are sent over an ATM VC in PE 1, the scheduling of data becomes hierarchical with two main levels: packet level scheduling and per-VC cell level scheduling.
At the first level, frames are queued on a per-CoS (or forwarding class), per-VC basis in order to achieve the proper class of service differentiation for the frames in the same VC. Each Ethernet frame is queued based on the VC dedicated forwarding class queue, as configured in the ingress classification profile. The packet level scheduling can make use of a hierarchy in order to enforce aggregate bandwidth among a group of queues feeding an ATM VC or to enforce aggregation of bandwidth across all queues of all VCs at a given customer site.
At the second level, the segmented cells are queued in per-VC queues according to the configured ATM service category and the traffic descriptor of the ATM VC. Scheduling at the ATM level enforces the priority and bandwidth sharing desired at the cell level. This architecture is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2 – Hierarchical scheduling into a ATM VC
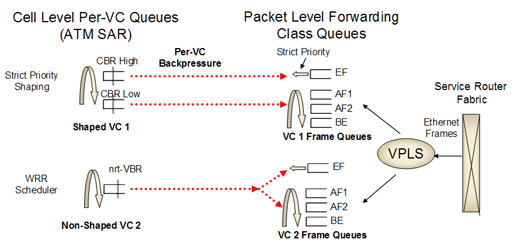
It is important to note that any discard decision should be performed exclusively at the packet level where the context for the frame forwarding class and for the 802.1p bit mapping to a forwarding class is known. When a per-VC queue backs up, a back-pressure scheme should be applied such that the frames are held in the per-forwarding class packet queues dedicated to this VC. There is, however, a condition under which a discard occurs in the ATM SAR device. This is when the CRC 32 check for a re-assembled AAL5 PDU fails. This occurs when a cell is missing or was re-ordered in the ATM network for a given AAL5 PDU.
This hierarchical scheduling of frames and cells of a given VC terminating on a VPLS instance provides the flexibility to apply policing and shaping on a per-forwarding class basis for the Ethernet frames of each VC, as well as the option to shape the aggregate cell flow into the ATM VC back into the customer site.
Resilience
Resilience of the ATM VC at the gateway PE router is provided via a SONET/SDH link automatic protection switching group. Furthermore, customer STP bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) are transparently passed from the TLS network to the VPLS network. This requires the translation of customer BPDUs from 802.1d format, which operates in the ATM TLS network, to the per-VLAN STP (PVST) format, which is typically used by customer premises equipment that is directly attached to a VPLS PE. This allows each customer to run STP end-to-end to prune the entire topology in order to select an active path and to disable loops.





